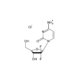
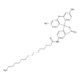
4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid
- SKU
- H0013
Category: Building Blocks, Intermediates, Reagents
- Synonyms
- 3-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-2-oxopropanoic acid , 4-HPPA, p-Hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid
- 156-39-8
- CAS-Number
- C9H8O4
- Molecular Formula
- 180.16
- Molecular Weight
Specifications
- Purity
- ≥98% (HPLC)
- Appearance
- Light yellow crystalline powder
- Identity
- 1H-NMR
Properties
- Solvents
- water, ethanol (50 mg/ml), ether, methanol
- Melting Point
- 219-220°C (lit.)(dec.)
- Boiling Point
- ~380.8 °C at 760 mmHg (Predicted)
- Refractive Index
- n20D 1.60 (Predicted)
- Density
- ~1.4 g/cm3 (Predicted)
Downloads
- Safety Data Sheet
- CDX H0013 MSDS.pdf
- Shipping
- AMBIENT
- Short Term Storage
- +4°C
- Long Term Storage
- -20°C
- Handling Advice
- Protect from light and moisture.
- Use / Stability
- Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
- Hazard statements
- H315-H319-H335
- Precautionary statements
- P261-P305 + P351 + P338
- GHS Symbol
- GHS07
- Signal word
- Warning
- Transportation
- Not dangerous goods
- Description
- Keto acid that is involved in the tyrosine catabolism pathway. It is a product of the enzyme (R)-4-hydroxyphenyllactate dehydrogenase and is formed during tyrosine metabolism. The conversion from tyrosine to 4-HPPA is catalyzed by tyrosine aminotransferase. 4-HPPA can be converted to homogentisic acid which is one of the precursors to ochronotic pigment. A deficiency in the catalytic activity of HPD is known to lead to tyrosinemia type III, an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by elevated levels of blood tyrosine and massive excretion of tyrosine derivatives into urine.
- Smiles
- OC1=CC=C(CC(C(O)=O)=O)C=C1
- InChi Key
- KKADPXVIOXHVKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- References
- (1) C.H. Doy, et al.: Nature 186, 529 (1960) , (2) W. Loffelhardt & H. Kindl , FEBS Lett 104, 332 (1979) , (3) K. Tomoeda, et al.: Mol. Genet. Metab. 71, 506 (2000) , (4) E. van Dyk & P. Pretorius , BBRC 338, 815 (2005)
- InChi
- InChI=1S/C9H8O4/c10-7-3-1-6(2-4-7)5-8(11)9(12)13/h1-4,10H,5H2,(H,12,13)
Keto acid that is involved in the tyrosine catabolism pathway. It is a product of the enzyme (R)-4-hydroxyphenyllactate dehydrogenase and is formed during tyrosine metabolism. The conversion from tyrosine to 4-HPPA is catalyzed by tyrosine aminotransferase. 4-HPPA can be converted to homogentisic acid which is one of the precursors to ochronotic pigment. A deficiency in the catalytic activity of HPD is known to lead to tyrosinemia type III, an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by elevated levels of blood tyrosine and massive excretion of tyrosine derivatives into urine.