Specifications
- Purity
- for microscopy
Properties
Downloads
- Safety Data Sheet
- CDX K0037 MSDS.pdf

Available from stock
Category: Non Fluorescent Detection & Chromogene Detection
“The Gram stain is a differential staining technique most widely applied in all microbiology disciplines laboratories. It is one of the most important criteria in any identification scheme for all types of bacterial isolates. Different mechanisms have been proposed to explain the Gram reaction. There are many physiological differences between Gram-positive and Gram-negative cell walls. Ever since Christian Gram has discovered Gram staining, this process has been extensively investigated and redefined. The Gram staining allows a fast differentiation of bacteria in Gram-positive and Gram-negative. The mureine structure of the bacteria walls is the basis of the color affinity. Bacteria will be stained with Gram’s crystal violet solution – an aniline dye – in the first step. After the treatment with iod solution, a dye-iod complex will form. During the decolorizing step, this complex stays in the multilayer mureine structures of the Gram-positive bacteria and they will appear blue. Gram-negative bacteria have a monolayer mureine structure only, the dye-iod complex does not stay bound to the cellwall, they will be decolorized. Gram-negative bacteria will be counterstained by safranin solution and appear orange.
| Synonyms | Gram Stain Kit, Bacteria Staining Kit according to Gram |
|---|---|
| Purity | for microscopy |
| CAS-Number | n/a |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | RT |
| Long Term Storage | RT |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use / Stability | This product should not be used if colour has changed or if there are |
| Hazard statements | H225-H319-H336-H351-H411 |
| Precautionary statements | P201-P210-P273-P280-P370 + P378-P391 |
| GHS Symbol | GHS02+GHS07+08+09 |
| Signal word | Danger |
| RIDADR | UN3316 |
| Transportation | Packing Group II |
| Quantity | 1 Set, Bulk |

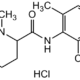 Mepivacaine hydrochloride
Mepivacaine hydrochloride