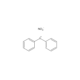
DAN
- SKU
- D0062
Category: Fluorescent Detection, Fluorescent Detection
- Synonyms
- 2,3-Diaminonaphthalene
- 771-97-1
- CAS-Number
- C10H10N2
- Molecular Formula
- 158.2
- Molecular Weight
Specifications
- Purity
- ≥98% (HPLC)
- Appearance
- Off-white to light brown solid
- Identity
- 1H-NMR
Properties
- Solvents
- DMSO, DMF or pyridine
- Melting Point
- 197-203 °C
- Fluorescence
- λex 364 nm, λem 406 nm in 0.5 M Na carbonate pH 10.0 (after derivatization with NaNO2 in 0.1 M HCl)
Downloads
- Safety Data Sheet
- CDX D0062 MSDS.pdf
- Shipping
- AMBIENT
- Short Term Storage
- +4°C
- Long Term Storage
- +4°C
- Handling Advice
- Protect from light and moisture.
- Use / Stability
- Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C.
- Hazard statements
- H302, H315, H319, H335, H350
- Precautionary statements
- P201, P261, P305 + P351 + P338, P308 + P313
- GHS Symbol
- GHS07+GHS08
- Signal word
- Danger
- Transportation
- Not dangerous goods
- Description
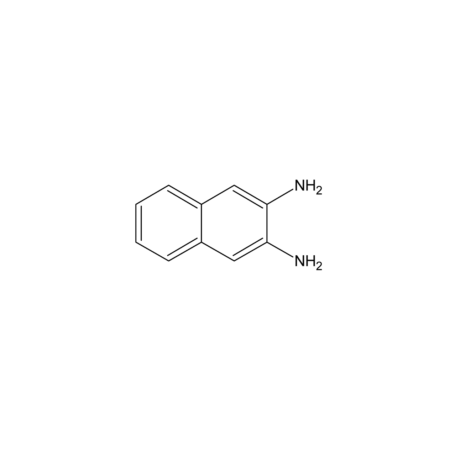
- The 2,3-diaminonaphthalene (DAN) assay is routinely used in the determination of nitrite/nitrate levels in biological fluids and cellular extracts as one indicator of nitric oxide activity. The assay, as reported by Misko, uses the reaction of DAN with NO2- under acidic conditions to form a detectable fluorescent naphthotriazole. The reaction proceeds at acidic pH at room temperature. Fluorescence is monitored following the addition of NaOH, which raises pH, resulting in lower background and increased sensitivity (Ex/Em: ~365/415nm). However, detection at 450nm is recommended to avoid fluorescent blanks and increase sensitivity. The fluorescent background of DAN is low for maximum sensitivity. Detection limits of NO achieved by this method are in the high-pM range. 2,3-Diaminonaphtaline (DAN) is used as a derivatisation-reagent for the determination of selenium at low detection limits. The 4,5-benzopiaselenol-complex can be quantified by photometry or GC.
- Smiles
- NC1=CC2=CC=CC=C2C=C1N
- InChi Key
- XTBLDMQMUSHDEN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- References
- (1) J. Pedro et al.: Anal. Chim. Acta 516(1-2), 229 (2004) , (2) T. Nagano et al.: Biol. Pharm. Bull. 21(12), 1247 (1998) , (3) W.C. Hawkes et al.: Anal. Biochem. 241(2), 206 (1996) , (4) R.F. Bayfield et al.: Anal. Biochem. 144(2), 569 (1995) , (5) P. Damiani et al.: Talanta 33(8), 649 (1986)
- InChi
- InChI=1S/C10H10N2/c11-9-5-7-3-1-2-4-8(7)6-10(9)12/h1-6H,11-12H2
The 2,3-diaminonaphthalene (DAN) assay is routinely used in the determination of nitrite/nitrate levels in biological fluids and cellular extracts as one indicator of nitric oxide activity. The assay, as reported by Misko, uses the reaction of DAN with NO2- under acidic conditions to form a detectable fluorescent naphthotriazole. The reaction proceeds at acidic pH at room temperature. Fluorescence is monitored following the addition of NaOH, which raises pH, resulting in lower background and increased sensitivity (Ex/Em: ~365/415nm). However, detection at 450nm is recommended to avoid fluorescent blanks and increase sensitivity. The fluorescent background of DAN is low for maximum sensitivity. Detection limits of NO achieved by this method are in the high-pM range. 2,3-Diaminonaphtaline (DAN) is used as a derivatisation-reagent for the determination of selenium at low detection limits. The 4,5-benzopiaselenol-complex can be quantified by photometry or GC.