Gram Staining – Fast Differentiation of Gram-positive and Gram-negative
CDX-P0023 25 mg | 500 mg | 5 g
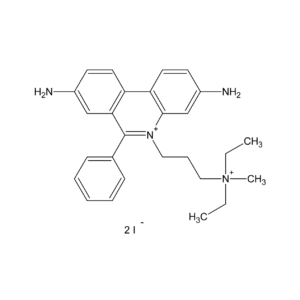
The most common red-fluorescent nuclear stain. Membrane-impermeant and generally excluded from viable cells. It can easily penetrate dead or damaged cells and as such is commonly used for identifying cell viability in a population or as a counterstain in multicolor fluorescent techniques. It binds to DNA and RNA by intercalating between the bases. Spectral Properties: lex 488-535 nm; lem 617 nm.
Other Cell Viability Dyes